A Guide To Understanding Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is one of the most common cancers that can affect individuals at any age. It typically starts from the inside of the bladder in the urothelial cells that line it. If detected in its early stage, bladder cancer can be treated and managed. To stay well-informed about one’s condition, one must speak to an expert and acquire resources that can help better understand bladder cancer and other associated factors.
What are the indicators of bladder cancer?
- There may be a number of symptoms during the early onset of bladder cancer. One may have blood in the urine, pain during urination, frequent urination, and back and pelvic pain.
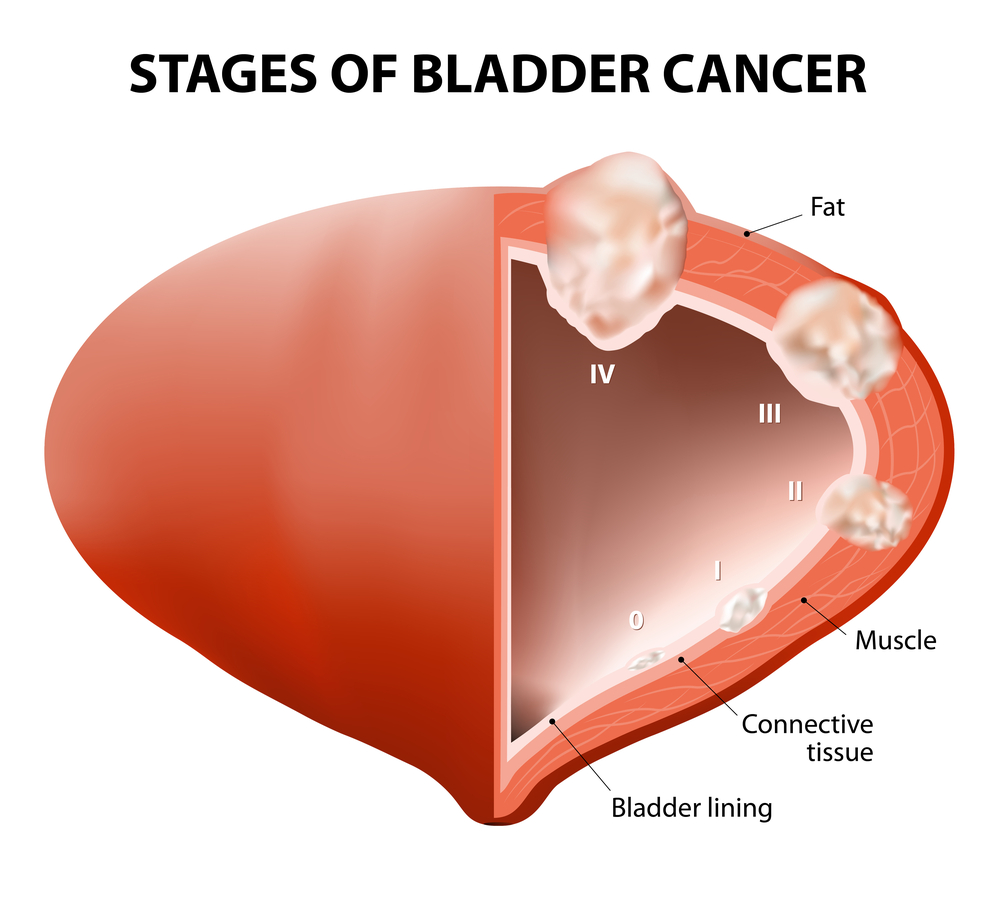
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
- Bladder cancer develops when the cells inside the bladder begin to grow abnormally. There are certain risk factors that may contribute to bladder cancer.
- Tobacco use, exposure to chemicals, radiation, irritation of the bladder lining, infections, etc. are thought to be some of the major risk factors for bladder cancer.
What are the different types of bladder cancers?
Broadly speaking there are three types of bladder cancers, namely:
- Urothelial carcinoma – One of the most common types of bladder cancers and arises from a tissue lining the hollow organs’ inner surface, known as the transitional epithelium.
- Squamous cell carcinoma – Squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder is usually detected in the advanced stages of bladder cancer, and the tumors are usually of high to moderate levels.
- Adenocarcinoma – Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder is not very common. Although areas that have an endemic Schistosoma haematobium, almost 10% of cancers of the bladder are non-urachal adenocarcinomas.
What is urothelial carcinoma?
- Urothelial cells are the cells that line the inside walls of the bladder. These cells also line the inside of the ureters and the urethra. These are also known as transitional cell carcinoma. These cells help the bladder expand and contract during filling up and voiding, respectively.
- Urothelial carcinoma can form in the inside of the bladder as well as the ureters and bladder. This is the most common form of bladder cancer in the country.
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
- Squamous cells are not common in the bladder and squamous cell carcinoma is a rare type of bladder cancer. However, if the bladder is subjected to irritation for a long time, the urothelial cells may turn into squamous cells. In advanced bladder cancer, this is known as squamous cell carcinoma. Moreover, like in any advanced bladder cancer, the symptoms mimic those of urinary tract infection (UTI) like dysuria, urgency in urination, frequency in urination, etc.
What is adenocarcinoma?
- This is a type of bladder cancer that affects the glands in the bladder that secrete mucus. Such type of advanced bladder cancer is rare in the country. However, adenocarcinoma of the bladder may arise from other organs like the prostate, endometrium, colon, rectum, cervix, etc.
- The problem with bladder adenocarcinoma is that it is usually detected only in the advanced stages of a bladder cancer.
How can the bladder be irritated?
- If a patient has been using a catheter for a long time or has suffered from a certain pathogenic infection, the bladder may get irritated.
- This can precipitate squamous cell carcinoma.
- However, squamous cell carcinoma is rare in the country as the particular parasitic infection is almost nil here.
What are the survival chances of a bladder cancer patient?
- The chances of survival of people suffering from bladder cancer are high in most of the cases. This is because most of the people suffer from carcinoma of the urothelial cells. This type of cancer takes time to develop and usually makes a strong presence with some symptom or the other, thus getting detected and treated in the early stages.
- If someone is suffering from squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma, the chance of survival depends a lot on advanced bladder cancer treatment. The earlier the doctor comes to know about it, the greater are the chances of survival. Advanced bladder cancer information is critical in managing cancer because as with time the cancer tends to grow and spread.

