An Overview Of Urinary Tract Infections
An overview of urinary tract infections
An infection affecting any part of the urinary system is called a urinary tract infection (UTI). The urinary system is composed of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, and the kidneys. Often the infections affect the lower urinary tract, which is made up of the bladder and the urethra. Women are at a higher risk of suffering from UTI as compared to men.
An infection that is limited to the bladder can be painful as well as annoying. However, if the UTI spreads to the kidneys, it can have serious consequences. Typically, a UTI is treating using antibiotics by doctors.
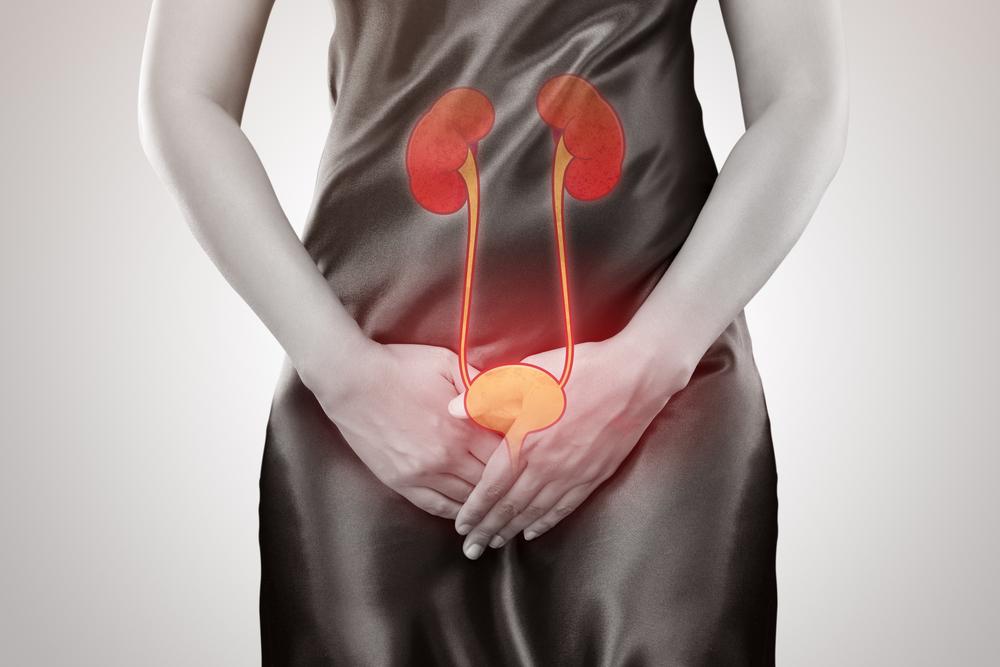
Below is some information about the symptoms of a UTI, its causes, and more.
What are the most common signs and symptoms of a UTI?
A UTI does not always show signs and symptoms. However, when it does, the symptoms may include:
- A constant and persistent urge to urinate.
- Frequently passing small amounts of urine.
- A burning sensation while urinating.
- Urine that looks cloudy.
- Urine that looks red, cola-colored, or bright pink (a sign of blood)
- A strong-smelling urine.
What are the causes of a UTI?
Typically, when bacteria enter the urinary tract, it leads to a UTI. The urinary system is supposed to keep out such bacteria; however, it sometimes fails. At such a time, the bacteria may take hold and develop into an infection in the urinary tract. The most common UTIs mainly affect women and occur in the bladder and the urethra. Some of the causes of a UTI are:
- Urethritis – Urethritis, which is an infection of the urethra, occurs when the GI bacteria spread from the anus to the urethra. As female urethra is close to the vagina, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like herpes, mycoplasma, chlamydia, and gonorrhea may cause urethritis.
- Cystitis – Cystitis, which is an infection of the bladder, is caused by the Escherichia coli (E. coli). Commonly, this bacteria is commonly found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. However, at times other bacteria can be responsible for cystitis. Cystitis may be caused by sexual intercourse, but one does not need to be sexually active to develop it. Owing to the female anatomy, all women are at a risk of suffering from cystitis.
What are the risk factors for a UTI?
Women are commonly affected by UTIs. Many women suffer from at least one infection in their lifetime. Risk factors for a UTI, specific to women, are:
- Menopause – After menopause, there is a decline in the circulating estrogen, which causes changes in the urinary tract. This makes a woman more vulnerable to a UTI.
- Sexual activity – Sexually active women tend to suffer from more instances of a UTI than women who aren’t sexually active. Additionally, having a new sexual partner also increases the risk of a UTI.
- Anatomy – Women have a shorter urethra than men. This shortens the distance that the bacteria need to travel to enter the bladder, making women susceptible to a UTI.
- Birth control – Certain types of birth control increase the risk of a UTI. Women using diaphragms for birth control are at a higher risk of a UTI than women using spermicidal agents.
- Other risk factors – Certain other abnormalities like urinary tract abnormalities, blockages in the urinary tract, usage of a catheter, a suppressed immune system, and a recent urinary procedure increases the risk of suffering from a UTI.
What are the best home remedies for treating a UTI?
Often, doctors use antibiotics to treat a UTI. Sometimes, antibiotics in low doses are used over a period of time to avoid a recurrence. A number of home remedies can be used to avoid infections as well as reduce the risk of a recurrence. Some of the best home remedies for treating a UTI are:
- Stay hydrated.
- Increase the intake of vitamin C.
- Drink unsweetened cranberry juice.
- Consume probiotics.
- Practice good bathroom and hygiene habits.
- Have natural supplements.

