Facts and Signs of Ingrown Hair
Ingrown hair affects everyone, irrespective of the gender. The hair on our skin naturally grows outward and above from the skin. There are two principal layers of our skin – the epidermal layer and the dermal layer. Hair grows from the dermal layer of the skin, which also contains rough connective tissue, sweat glands, blood vessels, and so on. Skin hair that rises to a certain extent from the dermal layer of the skin but ultimately curls around and recesses into the same instead of growing outward is known as ingrown hair.
Fun facts about ingrown hair
- Ingrown hair can be found in all age groups.
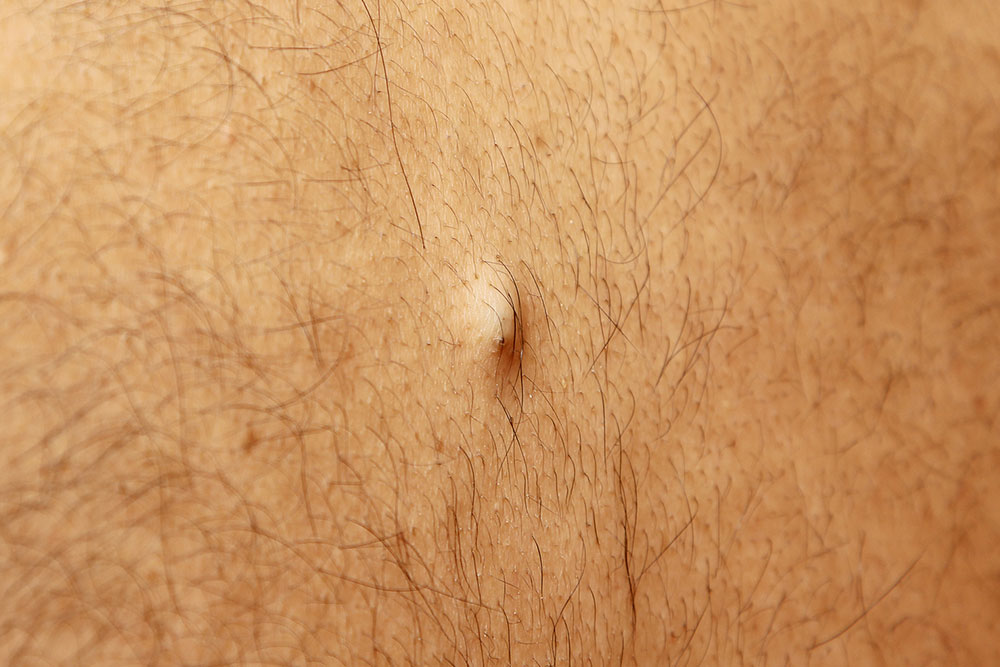
Source of ingrown hair
Teenagers and adults are more prone to developing ingrown hair and need removal techniques.
It is not unusual for human beings to develop ingrown hair at some point in their life.
Causes of ingrown hair
- Ingrown hair is mostly of natural occurrence in some people. It can either be present from birth, or it can be due to some external damage to the skin over time.
- An individual is said to have ingrown hair when the sharp end of the body hair twists back or develops laterally into the cutis of the hair follicle. So if such strands of hair are groomed too adjacent or beneath the follicular opening of the same, it causes a sharp tip to be formed. The latter can then penetrate the dermis and result in ingrown hair.
- As it is correctly said, improper and unhygienic shaving techniques like cutting too close or bruising the skin majorly contribute to the growth of ingrown hair.
- A lot of people go for waxing for ingrown hair removal. The hot wax not only irritate the skin with the ingrown hair, but wrong waxing techniques can also modify or enhance the growth of the ingrown hair.
- Just like waxing, putting on tight clothing exerts pressure on the skin and causes friction, which enhances the growth of ingrown hair.
- Hair has a chance to grow inward due to the continuous, aggressive, and improper removal of hair. Hair can also grow sideways if the natural pathway of its growth, that is, upward, is blocked by excessive dead skin cells, forming debris. The latter usually clogs the follicular openings of the hair, forcing it to grow another way.
Symptoms of ingrown hair
- Persistent itching and irritation.
- Ingrown hair removal can get worse after the body hair grows back.
- Staphylococcus is the skin bacteria that is largely found scattered on a healthy skin layer. In folliculitis, ingrown hair reacts with these bacteria, causing pustules and infection.
- Pink or red bumps on the skin are commonly formed due to the restricted foreign bodies’ unhealthy and provocative reaction owing to ingrown hairs.
- Immediately after shaving the skin, especially in the case of sensitive skin, dry reddish bumps or small pustules are common. If these are not treated with properly medicated creams and you repeatedly shave over the same, it can cause ingrown hair.
- Redness and tenderness.
- Light red bumps having reddish halo also indicate possible inflammation. Such bumps may center an ingrown hair in some cases. In other cases, the bumps usually cover the hair debris.
Ingrown hair does not pose serious threats to our mundane life, but they are definitely embarrassing and irritating when visible from the outside. Needless to say, they cause itching or irritation when in certain places of the body.

