Standard Methods Used for the Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis or DVT occurs when there is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in your body. Here is everything you need to know about the different methods used for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
When you have a blood clot in one of the deep veins, you are suffering from deep vein thrombosis or DVT. Typically, DVT affects the deep vein in your leg, and may cause swelling and pain in the leg without any other symptoms. You are at a higher risk of developing DVT, if you smoke, are overweight, lead a sedentary lifestyle, and are over the age of 60.
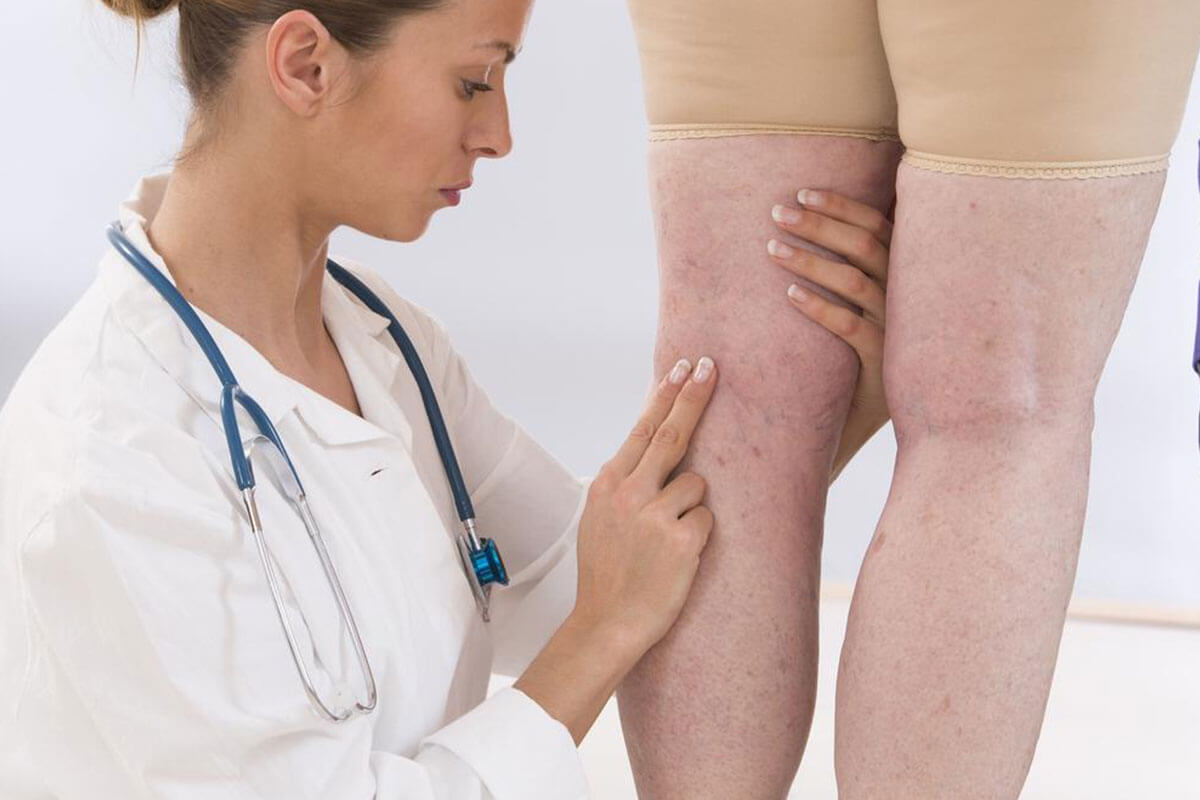
Deep vein thrombosis is considered to be a serious medical condition because if the blood clots break loose from your vein, they can travel to your lungs and block the blood flow there, leading to a life-threatening complication called pulmonary embolism. Therefore, it is crucial to be on the lookout for the signs and symptoms of DVT. DVT can show no symptoms in some of the cases, at least initially. However, when you do experience symptoms they will mostly be a pain in the leg that starts in your calf, and swelling in the leg that is affected.
Some of the risk factors that are associated with deep vein thrombosis include prolonged bed rest, surgery, inheriting a blood-clotting disorder, pregnancy, smoking, heart failure, age, and cancer. In order to confirm the diagnosis of DVT, you may have to have tests such as duplex ultrasound, MRI and venography. Duplex ultrasound is a painless diagnostic test that uses sound waves to produce pictures of your blood vessels to check for clots. You cannot use this test to find blood clots that are located deep inside your body like the pelvis. In venography, a radioactive dye in injected into the vein by a doctor, and then X-rays are taken to highlight the clot.
The treatment of deep vein thrombosis has several aims including preventing the clot from growing and breaking off as well as avoiding complications. Most often than not, medications are mainly used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, however, surgery may be required in rare cases. The standard methods that are used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis are:
- Anticoagulants
One of the medications that are used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis are blood thinners or anticoagulants. When you are prescribed these drugs, they help by reducing the clotting ability of your blood. Even though they may not break up the blood clots that already exist, they will definitely prevent any future clots and stop the clots from getting bigger. Some of the common anticoagulants used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis are heparin, warfarin, and rivaroxaban. It is critical that you do not take more that the prescribed dosage because these medications can have severe side effects. Pregnant women should stay away from anticoagulants.
- Compression Stockings
These are used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis to prevent the swelling in your legs. The pressure created by these stocking ensures that the chances of blood clot are reduced. It is recommended that you wear these stocking throughout the day for a period of 2 to 3 years.
- Filters
If for some reason, you cannot take medications like blood thinners, the doctor may insert a filter in your abdomen, into the vena cava. A filter in the vena cava stops the clots that break free from travelling to the lungs. This method used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis prevents the development of complications such as pulmonary embolism.
- Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis
If you are at a high risk for developing pulmonary embolism or have a clot in your arm, your doctor may prescribe catheter-directed thrombolysis. This method of treatment of deep vein thrombosis makes use of a thrombolytic agent that breaks up a clot quickly and restores the blood flow. However, this method is riskier than the others because there is a higher chance of side effects like stroke and bleeding problems.
These are the standard methods that are used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. The method that is ideal for you will be chosen by your doctor depending upon your overall health, the severity of DVT, and your personal preferences.

