Types and Treatment of Chronic Psoriasis
Is your skin itchy, inflamed, flaky or scaly? You are probably headed toward developing psoriasis! Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease of the skin that ranges from mild to severe. Those affected by chronic psoriasis develop scaly patches on their skin that are inflamed, itchy, and painful. Depending on the symptoms, psoriasis is classified into various types. Chronic psoriasis treatment is based on the symptoms and the extent to which it has spread.
Like all autoimmune diseases, there is no specific cause for chronic psoriasis. Contributing factors for chronic psoriasis are mental stress and anxiety, low self-esteem, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors.
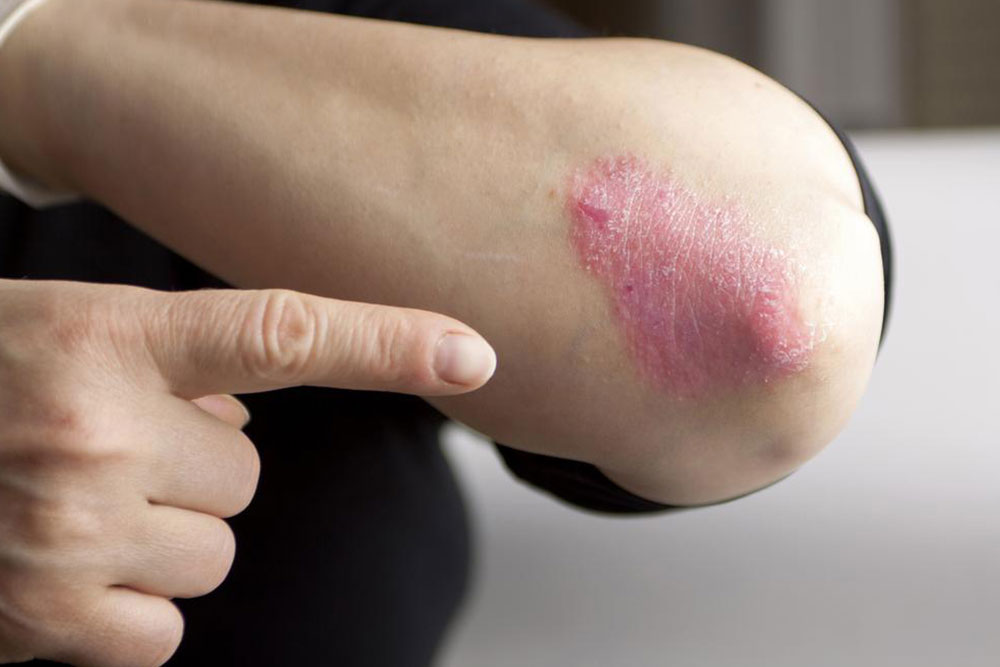
Common symptoms of psoriasis
Psoriasis occurs due to changes that occur beneath the skin rather than on the skin. Although psoriasis is classified into different types based on appearance and symptoms, the following are the common symptoms:
- Red patches on the skin
- Scaly, silvery patches
- Itchy skin
- Swelling of joints, stiffness or pain
If you need information on psoriasis and its symptoms, you should know that they are specific to the type of psoriasis.
Types of chronic psoriasis
Classifying chronic psoriasis helps in deciding the line of treatment.
- Plaque psoriasis – Plaque psoriasis is the most common form of chronic psoriasis. It is also referred to as psoriasis vulgaris. It is characterized by raised, inflamed, reddish skin covered by silvery white scales. It causes itching and burning sensations. Elbow, lower back, scalp, and knees are common places where plaque psoriasis occurs.
- Guttate psoriasis – This type of psoriasis commonly occurs in young adults and children. This type occurs in the form of tiny, pink-red spots on the skin near your trunk, upper arms, thighs, and scalp. Stress, skin injury, certain medication, or upper respiratory infections may act as triggers for guttate psoriasis.
- Pustular psoriasis – This is an uncommon type of psoriasis that occurs mainly in adults. It is characterized by pus-filled bumps that are surrounded by reddish skin. It may occur in one area of the body or cover the entire body (generalized pustular psoriasis), the latter occurrence requires immediate medical attention. Generalized pustular psoriasis may be triggered by topical medicine, stress, infection, exposure to chemicals or sudden stoppage of medication.
- Inverse psoriasis – Inverse psoriasis is characterized by bright, shiny, red skin devoid of scales. It usually occurs in armpits, under breasts, groin, and skin folds around genitals. This condition is worsened by scratching or sweating.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis – This is a very rare type of psoriasis, but manifests into a serious condition. It occurs almost all over the body and causes fiery skin that looks burnt. Severe itching or peeling, changes in body temperature, or faster heart rate is associated with this type of psoriasis. Complications like pneumonia, congestive heart failure may occur due to erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Nail psoriasis – Most people affected with some form of psoriasis have changes in nail structure. Psoriatic arthritis usually leads to nail psoriasis that causes pitting of nails, tender and painful nails, separation of the nail from the bed, changes in nail color, or chalk like deposits under nails.
- Psoriatic arthritis – This is a combination of psoriasis and arthritis. Characteristics of psoriatic arthritis are pain and stiff joints, sausage-like swelling of fingers and toes, and warm, discolored joints.
Treatment for psoriasis
Treatment for psoriasis depends on the type and severity. Various methods are listed below for various types of psoriasis:
Plaque psoriasis : Application of over-the-counter cortisone cream or ointment-based moisturizer to prevent dryness and irritation of skin is the first recommendation by the dermatologist. In some cases, light therapy may be needed. A combination of light therapy and ointment application can also be an option for this type of scalp psoriasis treatment.
Guttate psoriasis : The underlying infection is treated first for this type of psoriasis. Additionally, steroid creams, light therapy, and oral medications may be required.
Inverse psoriasis : Application of topical steroid creams, oral medication, and light therapy is the treatment protocol for inverse psoriasis. Medication to reduce bacterial or yeast growth also may be recommended.
Pustular psoriasis: Treatment depends on the size of the area affected. Corticosteroid creams are prescribed to treat this type of psoriasis. A larger area may require light therapy.
Chronic psoriasis can be treated based on the type of psoriasis. Although the root cause cannot be eliminated, chronic psoriasis treatment methods might help alleviate symptoms of the condition. The above pointers can help one to decide what should be done in case they experience any of the symptoms.

