What are the common and rare symptoms of Graves’ disease
An autoimmune disorder, Graves’ disease is a form of hyperthyroidism, i.e., it causes the thyroid gland to produce excessive amounts of hormones. It is one of the most common health conditions and usually affects women around the age of 40, but it is diagnosed among men too.
The exact cause behind the onset of this disease is not known, so it is hard to anticipate which people are most likely to contract it. As thyroid hormones influence several parts of the body such as body temperature, cognitive development, and nervous systems, it is vital to get it treated. If this condition is ignored for long, it can cause severe weight loss, intense mood swings, depression, and fatigue.
12 common symptoms of Graves’ disease
There are a few common symptoms of Graves’ disease that one should know about.
- Excessive perspiration
- Significant weight loss
- Increased or irregular pulse rate
- Shaking hands
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Sensitivity to heat
- Digestive problems such as diarrhea
- Erratic mood swings
- Goiter, i.e., swollen thyroid gland
- Changes in menstruation
- Sleep problems
Rare symptoms of the Graves’ disease
Apart from the common symptoms mentioned above, Graves’ disease has two primary types of rare symptoms as well. These are known as Graves’s ophthalmopathy and Graves’ dermopathy.
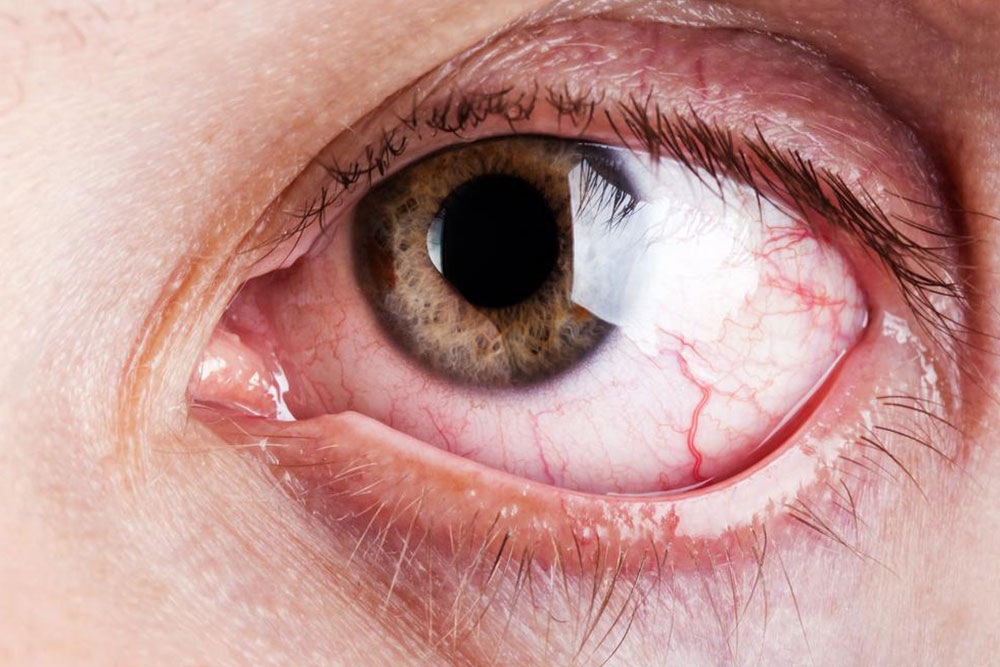
Graves’ ophthalmopathy – Roughly 30% of the patients suffering from the condition exhibit this symptom where the eyes are affected by inflammation.
- Exophthalmos, i.e., bulging eyes
- Experiencing pain or pressure in or around the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Redness of the eyes
- Loss of vision
- Double vision
- Swollen eyelids
Graves’ dermopathy In this situation, mostly the skin located on the shins or above the feet begins to thicken and redden. This condition can be improved with the help of OTC creams.
The stated symptoms of Graves’ disease may vary depending on the severity of the condition.
Diagnosis and treatment
To confirm the possibility of Graves’ disease, you will have to visit an endocrinologist. They will use diagnostic tools such as blood tests, x-rays, CT scan., radioactive iodine uptake, ultrasound and physical exam to identify the issues. When it comes to treating the disease, your doctor will recommend anti-thyroid drugs, radioiodine therapy and in rare cases surgery to alleviate the symptoms. Apart from medical treatment, your doctor will also encourage you to make essential changes in your diet and lifestyle.

